Long-term poor posture and muscle strain can easily lead to spinal problems, such as lumbar or cervical disc herniation. Mishandling of herniated intervertebral disc can be troublesome and should not be underestimated.
Where is spinal nerves?
The human spine is mainly composed of cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae, sacrum and coccyx, with a total of 33 sections. In addition to the first and second spine, there is a piece of cartilage between each spine, called an intervertebral disc. The outer layer of the intervertebral disc is fibrous tissue, and the inner layer is the soft cartilage named nucleus, which has the function of shock absorption, absorbing weight pressure and maintaining the normal movement of the spine. With age, the nucleus pulposus inside the intervertebral disc begins to become dehydrated and deteriorated , The annulus fibrosus also degenerates, which greatly reduces the pressure and shock absorption capacity of the intervertebral disc. If we are in a bad posture at all time, the continuous strain of the spine and muscles will inevitably lead to a herniated disc. Depending on where the herniated intervertebral disc presses the spinal nerve, the patient will have symptoms such as muscle spasm, pain, numbness, or pin and needle pain. In the entire spine, the focal point is at L5/S1. Disc protrusion of the lumbar spine can cause lower back, buttock and leg pain; disc protrusion of the cervical spine affects the shoulders, back and hands of patients. The symptoms and pain levels of patients are different due to the severity of the nerve compression.
MRI non-radiation examination monitor the intervertebral disc herniation treatment progress
There are many non-surgical conservative methods for the treatment of intervertebral disc herniation. To test the effectiveness and progress of the treatment, MRI scans can be used to compare before and after treatment, so that you can know whether the treatment is helpful and effective. It can be used to compare the progress of treatment.
Cox® Decompression Manipulation
A herniated disc does not come overnight. It takes a long time to treat the herniated intervertebral disc, so the treatment time ranges from three to six months. Patients should have patience and reasonable expectations. However, before COX® decompression manipulation short-term and long-term goals will be set with the patient. The short-term goal is limited to approximately nine to fifteen treatments in three to four weeks. It is hoped to achieve 30-50% progress, including arthralgia. Reduced and increased mobility. As for the long-term goal, MRI will be repeated after three to four months of treatment to check the progress of the disc herniation.
Before COX® decompression manipulation
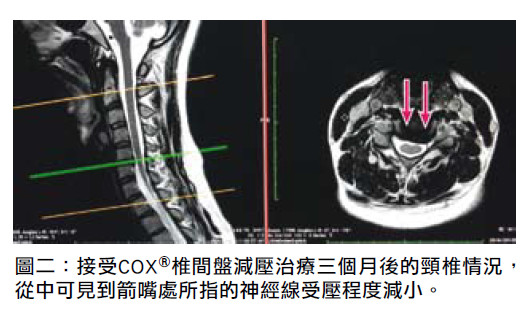
Three months after COX® decompression manipulation
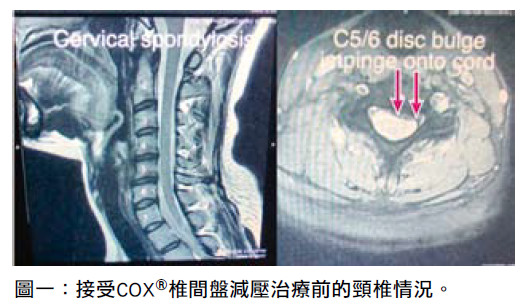
Before COX® decompression manipulation
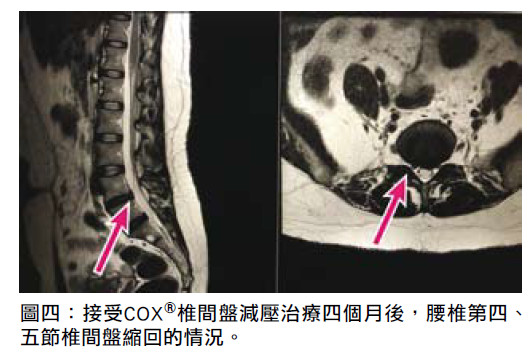
Four months after COX® decompression manipulation
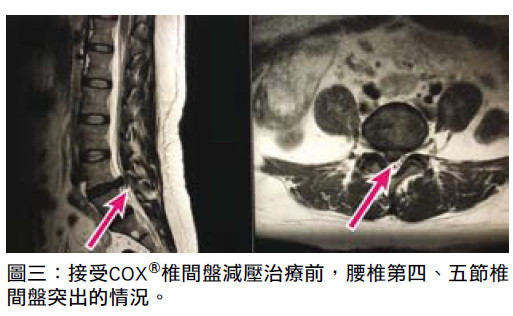
Three treatment stages of COX® decompression technic
The first stage is: acute inflammation
When the intervertebral disc is injured 2 to 7 days, the tissue around the intervertebral disc will become inflamed. This is a normal automatic repair function of our body to protect the intervertebral disc. If the patient can receive COX® decompression manipulation within 2 to 3 days after the herniated disc, the effect is very significant.
The second stage is: repair period
In the 3 to 14 weeks after the herniated disc, the collagen in the body will be produced around the soft tissues for repair. Intervertebral disc decompression therapy can guide the arrangement and distribution of collagen to repair the annulus fibrosus and make the intervertebral disc stronger. In terms of nutritional supplements, it is recommended to absorb water-soluble collagen to increase the body’s amino acids (Glycine and Proline) to help repair and rebuild the intervertebral disc tissue.
The third stage is: stabalization period
This stage ranges from 3 weeks to 2 years. Patients should maintain a good and correct posture and exercise to strengthen their low back.
Correct posture and improve living habits
Do not bend over to take objects, but squat down with your knees bent.
You should not bend over to wash your hair and stand with your back to the shower.
Do not cross your feet when sitting.
Do not sit for long periods of time and try to take short breaks. A back cushion supporting the low back should be added behind the seat to reduce lower back pressure.
Should not sit on low stools or on the ground.
You should not sit on a sofa that is too soft.
Do not sit on the bed with your feet straight to watch TV or read a book.
Sneezing and coughing will increase the pressure in the disc. You should tighten your abdomen as much as possible and press your hands to the abdomen to reduce shock.
If you sleep on your back, put a pillow under your knees. If you lie on your side, put a pillow between your legs.
Do not lie on your back and bounce up when you get up. You should turn your body to the side, rise in slow motion, and then lower your legs before standing.
Do not stand and bending forward or bending backward when doing any low back exercise. Avoid low back rotation on the left and right sides.

 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment


