
2019-05-16
Minimally invasive spinal decompression surgery via posterior cervical approach
In the last article, I have explained to the readers about the anterior cervical discectomy and fusion surgery. In this article, I will explain the minimally invasive cervical spine neurosurgery.
Surgical Treatment of Cervical Spine
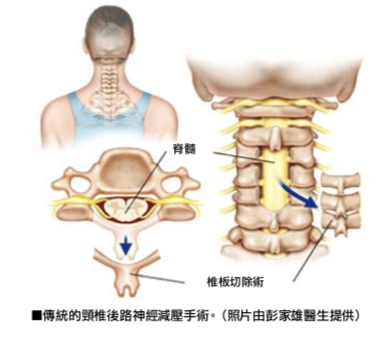
Minimally Invasive for Posterior Cervical Decompressive with mini-laminectomy for Spinal Cord is a surgical procedure to treat cervical spine nerve compression that’s due to pathological changes. The causes of the lesions are mostly from cervical disc herniation, thickening or ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) and Thicken Yellow Ligament due to degeneration, strain, injury or other diseases.
In cervical spinal stenosis, the cervical cord is compressed, which affects the central nervous system that is responsible for controlling the limbs, trunk, and bladder function. Therefore, in addition to the symptoms of spine instability, cervical spine patients also have symptoms of neurological deficit. Instability of the cervical spine can cause muscle spasm, neck and upper back pain, shoulder aches and headaches. Nerve compression will cause sensory nerve and motor nerve dysfunction. Patients will experience numbness and pain of the hand and foot, muscle weakness, unsteady gait, frequent urination, nocturia and difficulty in bowel movements, and constipation. In addition, the dysfunction of the reflex nerve and the sympathetic vagus nerve can also cause dizziness, tinnitus, gastrointestinal discomfort and even emotional instability.
The removing the time bomb from Mr. Zhang
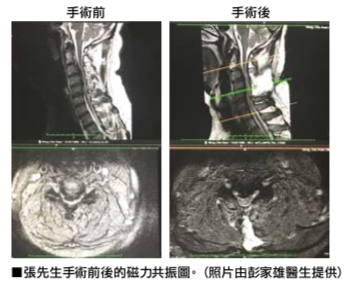
Mr. Zhang, 46 years old, works in an outdoor high-altitude manual labor on a construction site. In March 2017, he started to feel numbness and pain in his hands and feet. The body temperature on his left and right hands felt different and his hands and feet were occasionally weak. When walking, he felt weak and unsteady gait. MRI medical angiography confirmed severe degeneration of the c3-6, herniated disc, thickening of the posterior longitudinal ligament and ligamentum flavum, the cervical spine foramina very narrow, the cervical cord was severely compressed, and the spinal nerve was deformed and flatten. And there is affecting breathing, is controlled by C3-5. Therefore, Mr. Zhang’s central cord was compressed, deformed, flattened, and severely edema. There was a fatal risk of sudden breathing stop and paralysis of the limbs and lower body.
Due to the patient serious condition, some doctors advised Mr. Zhang to perform posterior cervical decompression and cervical fusion surgery. The surgery requires six to eight centimeters of cutting wounds to remove the patient’s lamina, spinous process and Ligamentum Flavum to achieve the effect of nerve decompression, and then Use titanium screws to stabilize Mr. Zhang’s cervical spine. However, Mr. Zhang considered that there will be a long surgical scars behind the neck in the future, and the operation will also cause the neck muscles to spasm, pain, muscle weakness and atrophy. In addition, the range of motion of the cervical spine will be greatly reduced after fusion, which will affect his working ability, so he refused the doctor’s surgical recommendations.
Mr. Zhang spent more than a month trying Chinese and Western medicine, chiropractors, physiotherapy, acupuncture and other alternative medicines. His condition did not improve, but it went from bad to worse, and he even had difficulty in daily activity and walking. Mr. Zhang went to the author’s clinic for consultation, he said that for many days he had difficulty even holding pens and chopsticks, and he also stumbled on several occasions. The problem of his cervical spine is like a time bomb, as long as there is a slight injury, it will permanently damage the spinal cord and cause quadriplegia. This time bomb should be removed as soon as possible.

There is a big difference between traditional surgery and modern surgery
In order to relieve Mr. Zhang’s doubts about the traditional surgery, the author suggested that Mr. Zhang should undergo neurosurgery with minimally invasive cervical decompression surgery. In order to ensure that the patient’s nerve function is fully protected, during the four-hour operation, the neurosurgeon will use a microscope and intraoperative nerve function conduction monitoring. When using a microscope throughout the entire process, the doctor will use his skilled fingers and sophisticated neurosurgical instruments to open a tiny wound of only one to two centimeters with an amplitude of less than two millimeters. The doctor will then operate in between the back neck muscles of the patient to ensure that the back neck muscles are not damaged at all. Under the flexible microscope technique, the doctor’s fingers will carefully remove a small amount of cervical lamina, hypertrophic ligamentum flavum and hyperplastic bone spurs under the amplitude of one to two millimeters, so as to safely decompress the patient’s cervical cord.
During the nerve decompression operation, through the entire nerve function and conduction monitoring test, the doctor will find that the patient’s electrical signal from the brain, through the cervical cord, and then to the limbs, the nerve conduction function appears after the successful decompression operation significant improvement. You should know that the primary task of a neurosurgeon is to protect the central nervous system. Compared with brain surgery (the doctor needs to use the brain stem at the base of the skull, the central nerve line as fine as a hair, and the narrow space in the cerebral arteries to do surgery), minimally invasive cervical neurosurgery is quite safe and low-risk.
The doctor will plan the most appropriate and safe medical plan according to the patient’s condition. From Mr. Zhang’s case, we can distinguish the difference between traditional posterior cervical surgery and the new minimally invasive neurosurgery. The wound is only one to two centimeters. The difference between a small wound and to a six to eight cm wound. the minimally invasive surgery will not damage the back neck muscles and ligaments of the patient, and the connecting ligaments between the bones and bones are preserved, so the surgery will not cause the neck muscles pain, atrophy and weakness. In conclusion, minimally invasive cervical spinal neurosurgery decompression surgery on the posterior cervical spine can radically cure the patient, so that the patient can recover as soon as possible, enjoy a normal life and return to work.

 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment


