2017-3-12
Accidentally hitting the cabinet with the head or accidental injury, causing the head to be shaken or injured, is often ignored. Patients often notice discomfort three weeks to three months later and consult a neurosurgeon.
More than 200 patients with traumatic brain injury have been analyzed clinically, and half of them do not remember any experience of head shaking or trauma. Head shaking or impact is easy to see in daily life, ranging from scalp trauma, to unconsciousness and life-threatening. In a car accident or accidental fall and bumping to the head, please do not think that there is no need for examination, diagnosis and treatment if there is no bleeding or trauma. The common clinical intracerebral hemorrhage is a case of brain trauma with no external wounds. If the head has been shaken or hit, the patient and family members should pay attention to several points, such as whether there was a temporary loss of consciousness or partial memory loss during the injury; observe whether the injured person is conscious and last for more than three days; whether the headache and vomiting symptoms are getting severe; Whether there is numbness or weakness on one side of the hands and feet; Whether the walking gait is unstable, the instability may be caused by cerebellar injury; When the patient with brain trauma sleeps at night, family members should call each other to ensure that they are awake at intervals to avoid intracerebral hemorrhage and blood compresses the brain, causing drowsiness and unconsciousness.
Assessment classification of head trauma
The Glasgow Coma Scale Coma Index is a method to assess the patient’s consciousness. The maximum score is 15 points, and the minimum score is 3 points. The scoring method is based on the patient’s eye-opening (Vision ), limb movement (Motor) and language response respectively. The sum of the three items is collectively called the Glass High Coma Index. Within 20 minutes after head trauma, the Glas high coma index of the patient’s consciousness is divided into:
(1) The Glas high coma index for mild head trauma is 13 to 15 points.
(2) With moderate head trauma, the Glass High Coma Index is 9 to 12 points.
(3) For severe head trauma, the Glass High Coma Index is 8 points or less.
Computerized tomography (CT Scan) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have been widely used. Especially in the application of CT, various acute intracranial hematomas, brain trauma, and cerebral edema can be clearly displayed on CT images. At present, in addition to the X-ray imaging of the skull, patients with head trauma should arrange CT examination as soon as possible for cases of unconsciousness, neurological dysfunction, and suspected intracranial hematoma.
Common types of head trauma
(1) Scalp hematoma: After head impact, most will swell up like an egg and become very painful. This condition usually disappears within a month and a half without applying any medicine, rubbing, or applying heat.
(2) Scalp wounds: The wounds need to pay attention to hemostasis and keep it clean.
(3) Headache: Headaches after head trauma vary greatly. Some people have only mild headaches, some people have unbearable headaches, some have persistent headaches, some have bouts of pain, some have dull pain, and some are like blood vessels. Pulsating pain, some people feel it like a burning pain, and some people feel it like being pressed by something. The scope of the headache may cover the entire head, or it may be limited to some specific parts. Headaches are often exacerbated by posture changes, stress, fatigue, or exertion. Rest or general analgesics can relieve headaches temporarily.
((4) Dizziness: dizziness after head trauma is usually intermittent. It is maintained for about a few minutes at a time. Changing posture can cause dizziness, and psychological stress can also induce dizziness. Dizziness can be improved when lying down and resting with eyes closed. There is considerable variability in the frequency and severity of dizziness attacks. After a mild head injury, about half of the patients experienced dizziness, and about half of them lasted more than two months. About three-quarters of dizziness patients have headaches, and about three-quarters of headache patients also have dizziness.
(5) Concussion: Minor concussion refers to the absence of any head trauma, but after a heavy blow to the head, there may be temporary loss of consciousness, hearing and smell, or temporary memory loss, headache, dizziness, and unconsciousness. Clear, blurred vision, unsteady walking, tinnitus, nausea, insomnia, inability to concentrate, emotional distress, and inability to lift the spirit at work. This situation should not be ignored. See a neurosurgeon for diagnosis and treatment. Proper treatment will have permanent sequelae.
(6) Brain trauma: There is substantial damage to the brain near the impact site, and intracranial hemorrhage is common. In addition to the related symptoms of concussion, the severity of brain trauma can cause drowsiness, coma, withdrawal, limb weakness, behavior or personality abnormalities, shortness of breath, etc.
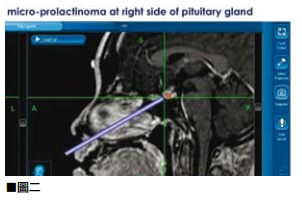
(7) Intracranial hemorrhage (cerebral hemorrhage): The hematoma directly compresses the cranial nerve tissue and causes damage, which can cause headache, vomiting, shortness of breath, twitching of the face or limbs, dizziness, weakness of the limbs, numbness, and changes in consciousness, lethargy, unconsciousness, Failure to seek medical treatment in time will cause permanent disability or life-threatening. In head trauma cases, the most common fatal complication is “subdural" or “supperdural" hemorrhage.
What is chronic subdural hemorrhage? If the patient with brain trauma is an elderly or young child, especially an elderly over 50, who accidentally slips on the toilet because he gets up at night, or if he walks unsteadily, falls and hits his brain, he may have a chronic subdural hemorrhage. It often appears slowly after two weeks of injury, and some people even take up to two years. Patients are prone to headaches or unilateral weakness, similar to strokes, and memory loss. Injuries to the cerebellum can also cause symptoms such as weakness of the feet on both sides, unstable walking, and poor appetite. However, electrolyte imbalance can also cause weakness in hands and feet, and many elderly people delay seeking medical attention. Basically, the incidence of chronic subdural hemorrhage is low, usually about 1 to 3%. Generally, the brain can absorb blood by itself. Once severe bleeding and long-term pressure on the brain stem, if it fails to promptly use minimally invasive surgery to drain the bloodletting water to help Decompression of the brain easily causes respiratory depression of the patient, which may cause permanent disability or life-threatening.
What is epidural hemorrhage? Because the blood vessels in the skull are bleed after being impacted, the dura mater itself is the outer layer of hard tissue that protects the brain. If the bleeding is not severe, it will be in the first few days of head trauma (average four to five days) Unusual signs of severe headache will appear, and even some patients are diagnosed with “migraine" or “tension headache" for treatment. Therefore, patients with clinical headache symptoms should also be informed of the history of head trauma doctor, so that the doctor can make a clear differential diagnosis.
(8) Brain laceration and skull fragments: direct damage to the tissues, the symptoms are the same as brain trauma and intracranial hemorrhage.
(9) Cerebral edema: edema often occurs after brain cells are injured, causing central nervous system damage and intracranial hemorrhage.
(10) Cerebral ischemia: Insufficient blood supply is often caused by increased intracranial pressure, causing brain cell damage or death.
(11) Epilepsy: about 2 to 7% of patients with brain trauma may have epilepsy symptoms, especially those with moderate to severe brain injury have a higher chance of epilepsy. At this time, it is necessary to observe whether the brain waves are abnormal. If it is severe epilepsy, it is necessary to take anti-epileptic drugs to control.
72 hours after a head injury is the most important observation period, patients and their families need to pay special attention. If the patient has the following symptoms, he should contact the neurosurgeon as soon as possible or go directly to the hospital for further examination:
(1) Whether there was a temporary loss of consciousness or partial memory loss when injured.
(2) Severe headache or dizziness.
(3) Lethargy or inability to wake up (such as gradually becoming unconscious).
(4) Indifferent to the outside world, lack of concentration or personality changes.
(5) Loss of orientation towards time and place.
(6) Nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
(7) Whether there is numbness or weakness on one side of the hands and feet.
(8) Whether the walking gait is unstable.
(9) Family members of patients with brain trauma should pay close attention to them when they go to bed at night. They should call each other at intervals to ensure that they are awake, so as to avoid intracerebral hemorrhage and blood pressure on the brain, causing drowsiness and coma.
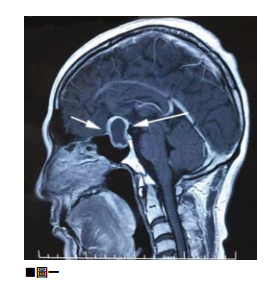
llustrated 01
The so-called supradural hemorrhage refers to the bleeding of the intracranial blood vessels after the head is impacted. Because the dura itself protects the outer hard tissue of the brain, if the bleeding is not severe, it will appear only four to five days after the injury. Unusual severe headache.
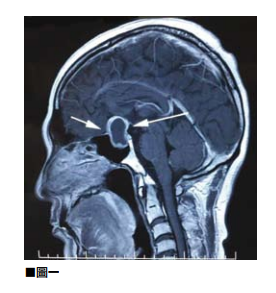
Illustrated 02
In a car accident or accidentally falling and hitting your head, don’t think that there is no need for examination, diagnosis and treatment if there is no bleeding or trauma. The common clinical intracerebral hemorrhage is a case of brain trauma with no external wounds.


 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment


