
2014-03-22

Acute low back pain
The most common pain patients experience are acute low back muscle or muscle sprain. Because muscles are the first line of defense to protect our spine, muscle injuries are the most common.
Causes
Most of the time, it’s because we accidentally do bending that cause muscle injuries, such as: sudden movement; bending and twisting at the same time; bending and lifting heavy objects on the ground are easy to cause muscle strain.
The pain that trigger muscle trauma is when we bend down to put down the heavy objects, because when we bend down, our low back muscles will lengthen, and at the same time we lift heavy objects, the low back muscles tighten to exert force. At the moment when the heavy object was put down, the force applied with the low back movement caused the low back to stretch too much, causing slight or severe muscle tears (depending on the weight of the object and the coordination of the movement).
Symptoms
Patients with acute low back pain usually feels a tingling at the moment of the sprain, but the tingling feeling will temporarily disappear after a short rest. By the next morning, the patient felt severe pain, stiffness, inability to move and muscle tension in the low back. Walking very slowly, slightly bent back and sideways, usually unable to straighten the low back and get up after sitting down. They also can’t stand and sit comfortably. Some patients also feel low back pain extending to the back and buttocks, and bending forward is very painful. If the soft tissues or joints are injured, the situation becomes serious. The muscles will continue to undergo a cycle of muscle inflammation slowly from acute low back pain to a chronic low back pain.
Understand the cyclic relationship of suffering from myositis
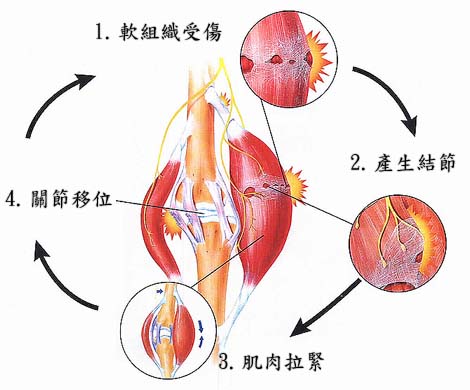
Soft tissue injuries-When muscles, ligaments and tendon are injured, they become weakened, strained and inflamed. Some slight tears will occur in these soft tissues.
Nodules (Trigger Points)-When the torn soft tissue is healed, the underlying fascia will become strained and twisted. New fibers will grow on these deformed and twisted fascias, making the position extremely hard and producing scars, which are called nodules (trigger points). When you press on these nodules, you will feel pain, or make other parts of the body feel painful.
Muscle Tension-After injury, the new fibers formed are not elastic, so the muscles will become stiff and tight, which will greatly reduce the mobility.
Joint misalignment-Because these tightened muscles are on the joints, they will also cause joint misalignment making it difficult to move around.
Treatment
After the treatment is completed, proper lumbar exercises should be done to strengthen the muscles and the strong soft tissues to avoid repetitive lumbar injuries. Remember, do not rely on long-term anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers to treat muscle pain. These drugs can only be used for pain relief and anti-inflammatory effects a few days after the injury. If long-term use not only prolongs the process of muscle recovery, but also increases the injury of the muscles. Because often when we take painkillers, we all feel the pain in the affected area disappeared, thinking that we have recovered and can move freely. But many times, there are problems with the rehabilitation procedures here, so that the affected area cannot be fully or completely recovered. We should find out the root cause of the pain, and then fix it.

 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment


