

Cervical Dystonia
Case Sharing
Ms. Huang, 33, who works in the design industry, started to experience neck pain in 2005. At first she thought her muscles were fatigued, because she felt better after resting.
After a period of time, her neck pain not only did not get better but also became severe. She gradually realized that her neck could not turn to the right, and her head naturally turned to the left. If she wanted to turn to the right, her right neck muscles would tighten and her head would keep shaking. And returning to the left, preventing the cervical spine from turning to the right. The face and neck can only be fixed on the left side.
Later, Ms. Huang continues to have headaches, she had 2-3 headaches every week, and there would be tinnitus in her right ear. In X-rays, the C5,6 were moderately degenerated, and the cervical vertebrae were all straight and slightly curved to the left. After detailed examination, it was diagnosed as “cervical dystonia".
The patient began to receive treatment in July 2009. Now the neck pain has been greatly improved. The patient’s head rotation can be controlled by herself, and the frequency of head and neck tremor has also been greatly reduced.
Symptoms
The patient’s head and neck can only be in one direction. If you want to turn the head in the opposite direction, the neck muscles will tighten, preventing the cervical spine from rotating, and the patient’s head will also vibrate. The patient’s symptoms will also increase when under pressure. On the contrary, They will be more comfortable during rest and sleep. In addition restricting the movement of the cervical spine, 80% of patients also feel neck pain. As many as 33%-40% of patients have head shaking, hand shaking or both
Pathological Analysis
Cervical dystonia is a type of constrictive torticollis, in neuropathy, it is a form of active dysfunction. The pathological cause is unknown, it may be related to the disorder of the “basal ganglia" (the basal ganglia is responsible for the control and regulation of muscle self-control activities in the brain). Other studies have shown that it may be caused by an imbalance of neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitter is a chemical substance released from the terminals of nerves, this substance will pass to the muscles to transmit information, but if this neurotransmitter is too heavy, it may cause excessive contraction of some muscles and cause muscle cramps.
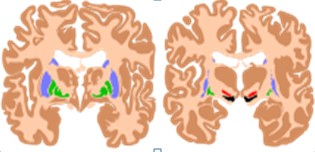
基底神經節 (圖中藍、綠、紅部份)
Treatment
Since there is no cure for this disease, the treatment is mainly aimed at relaxing the muscles and stimulating the cervical spine nerves, and using cervical spine decompression therapy and manual correction to help patients relieve pain. Patients are also encouraged to do various stretching exercises to increase joint mobility. Other treatments include the option of “BOTOX” injection to control the muscles, because the drug effect will disappear over time, patients must continue to inject Botox. If the patient’s condition is severe and conservative treatment is not effective, surgery may be required to remove the nerve cells in part of the contracted muscle.

 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment


