

Shoulder pain and tendonitis
Our shoulder joint is one of the largest and widest areas of motion in our body. If there is a problem with the shoulder joint, it will cause the fingers and arms to be unable to perform basic movements.
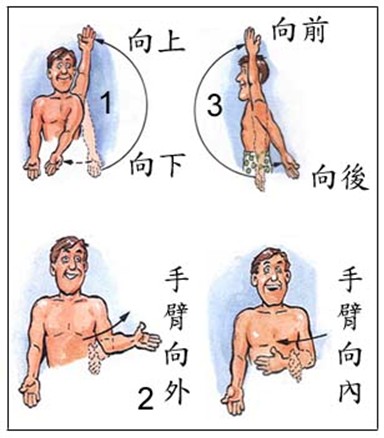
A normal and healthy shoulder can help our hands perform the following actions:
- Lift up and down (the first figure shown figure below )
- Forearms inward and outward (the second shown in the figure below)
- Hand forward and backward (the third shown in the figure below)
Causes of shoulder pain
Overwork or too little movement of the shoulder can cause pain and tension in the shoulder area, which will greatly reduce the ability of shoulder movement. When the shoulder movement is reduced, the muscles around the shoulder are also weakened and the joints of the shoulder are stiff, which leads to increased pain and immobility of the shoulder.
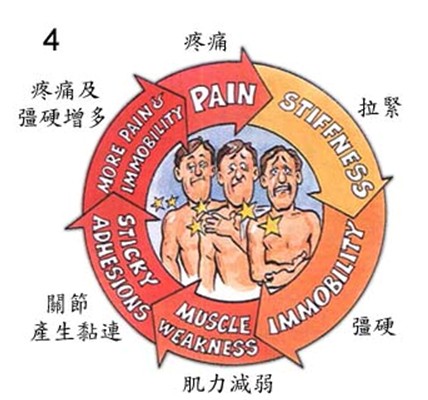
The causes of shoulder pain can be roughly divided into 5 categories
(1) Nerve reflex pain
Shoulder pain can be considered a reflex pain caused by the compression of the cervical nerves. Or there may be problems with internal organs which causes shoulder reflex pain. This kind of shoulder pain is generally sharp pain, and the pain will increase in intensity.
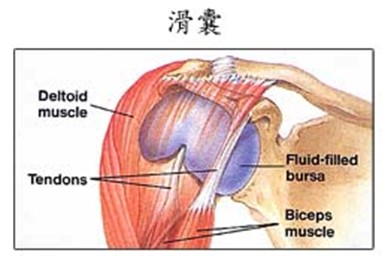
(2) Tendinitis or bursitis
Lifting heavy objects for a prolonged period of time and repetitive shoulder movements can strain the synovial membrane and tendons of the shoulder. The pain of tendonitis is less than the nerve reflex pain, which patients can usually point out which part of shoulder is painful, and shoulder mobility is reduced. If tendonitis is not treated as soon as possible, the pain will increase and the motility will decrease greatly until the hand cannot move.
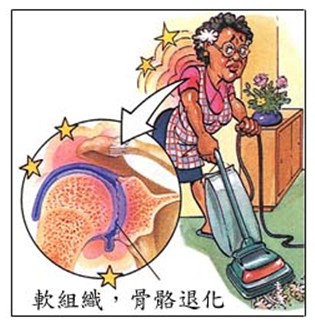
(3) Degenerative arthritis
As we get older, the functions and joints of the body will gradually degenerate. The bones, soft tissues and periosteum of the shoulders will also be affected. Pain will be triggered by certain movements, and it will generally get better after resting.
(4) Shoulder quadriceps trauma
Shoulder tendons become inflamed, torn or strained due to injury, any shoulder movement will cause pain, and shoulder mobility will decrease. If the tendon tear is severe, the chiropractor will refer the patient to the orthopedic for surgery.

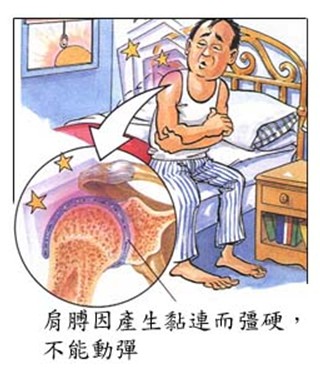
(5) Frozen shoulder
When the shoulder is unable to move and in pain, to avoid pain we try to minimize the shoulder movement. In this case, our shoulders will gradually stick together, which will increase pain and become unable to move. Patients cannot raise their arms for simple movements such as combing their hair, raising their hands, etc. The pain is usually tingling and stiff.
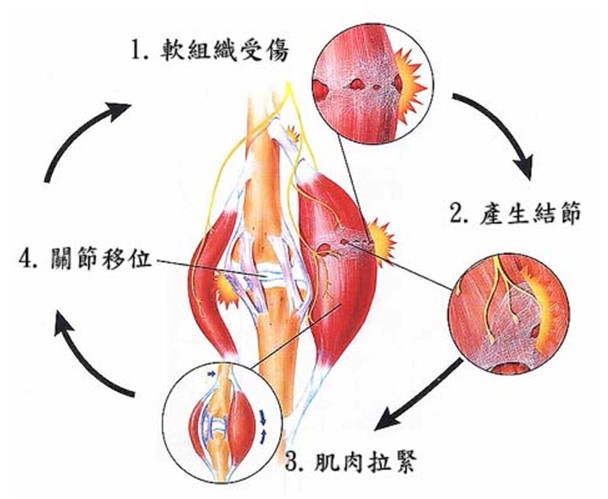
How does myositis happen?
(1) Soft tissue injury
When muscles, ligaments and roots are injured, they will gradually become weak, strained and inflamed. And will also have slight tears in these soft tissues.
(2) Produce nodules
After the torn soft tissue is recovered, the underlying fascia will become tight and twisted. New fibers will grow on these deformed and twisted fascias, making the position extremely rigid and producing lumps, which are called nodules (trigger points). When you press on these trigger points, you will feel pain, or reflex pain in other parts of the body.
(3) Muscle tightening
After an injury, the new fibers that grow on the soft tissues are inelastic, and the muscles become stiff and tight, greatly decreasing their mobility.
(4) Joint displacement
Because these tightened muscles are located on the joints, they will also cause the joints to get stiffness and affect any movements.
Chiropractor treatment for myositis
When facing the above symptoms, chiropractors will carefully examine the cause of the patient’s shoulder pain, and diagnose the source of the disease through vertebral functional examination, spinal mobility test, bone examination, nerve reflex examination and palpation. If necessary, X-ray tests or MRI scanning will be done to confirm the diagnosis. When necessary, chiropractors will also refer patients to other specialized medical departments. Chiropractors mainly use hand therapy and correction methods to relieve compressed nerves and tense muscles, and then use transfer aids to increase blood circulation in the affected area, whilst also instructing patients to do shoulder exercises to strengthen the surrounding soft tissues.

 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment


