2017-02-17
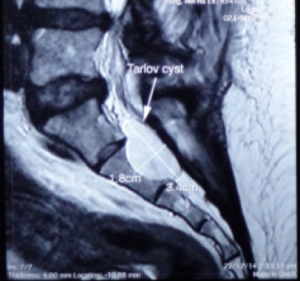
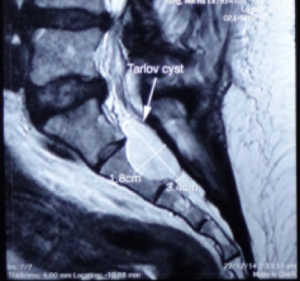
3.4 X 1.8 cm 骶骨第二節骶管襄腫
Tarlov Cysts
Usually incidental finding in lumbar MRI, one or more Tarlov Cysts will be found in the sacral spinal canal. If they are smaller than 1cm, the patient may not have any symptoms. But if the tarlov cyst grow to more than 1.5cm and it compressed the nerve, this may cause discomfort in patient.
What is Tarlov Cyst
Tarlov cyst generally find at the first to the third section of the sacrum and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The swelling can gradually increase and cause the cauda equina nerve to be compressed, causing nerve root inflammation or myelopathy and even affecting the bony structures. Magnetic resonance imaging can clearly distinguish the location, size, and relationship with the dura and nerve roots of the sacral canal.
Symptoms
The symptoms of tarlov cyst are similar to those of intervertebral disc herniation. It can also cause back and leg pain, paralysis, muscle weakness and stiffness, nerve irritation. But the most different is that the pain caused by tarlov cyst is mainly irritate the inner thigh, inner calf, back of the calf, plantar or around the anus, and the pain is variable, often occurring in different parts of the feet. In general, when patient lying down the symptoms will be relieved, and it will be aggravated by standing and walking for a long time. Pain and arthralgia can be aggravated by coughing or sneezing.
Treatment
Generally, small tarlov cyst will not cause any problems. However, if the patient’s symptoms cause nerve defects and seriously affect daily life, surgical intervention may be the best choice. The operation is processed by a neurosurgeon. A minimally invasive operation is performed to take out the cerebrospinal fluid from the cyst, then block the spinal fluid from entering the cyst, and then take the patient’s body fat or muscle to fill the pocket space.
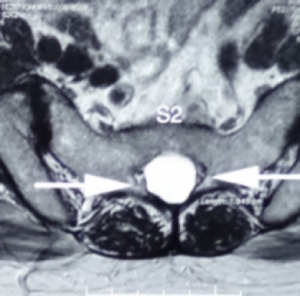
3.4 X 1.8 cm 骶骨第二節骶管襄腫
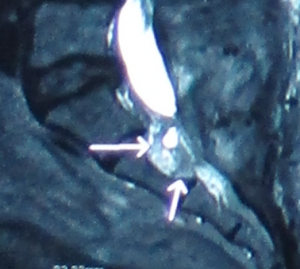
圖一
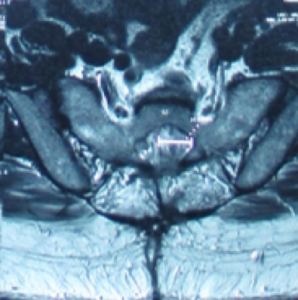
圖二
*For any enquiries about Chiropractic, please call 2804 6700
Data subject: Dr. Peng (neurosurgeon)

 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment


